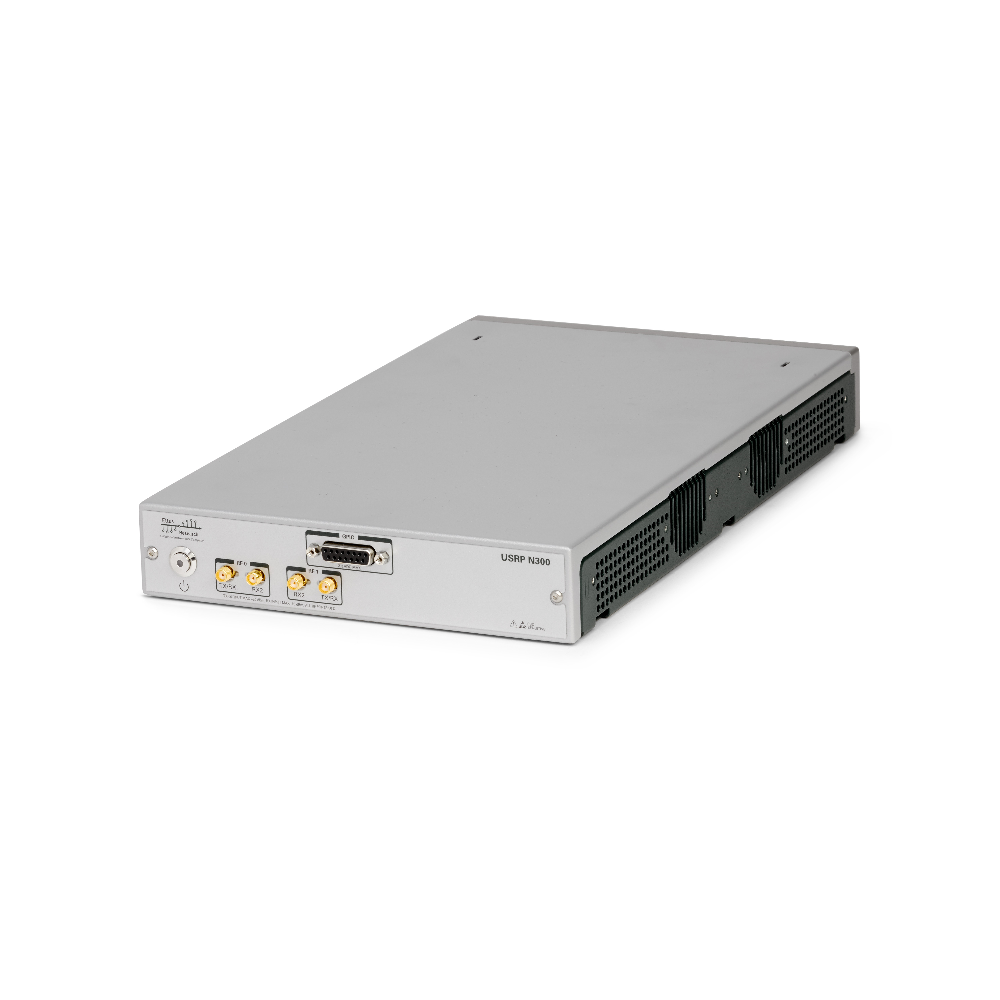
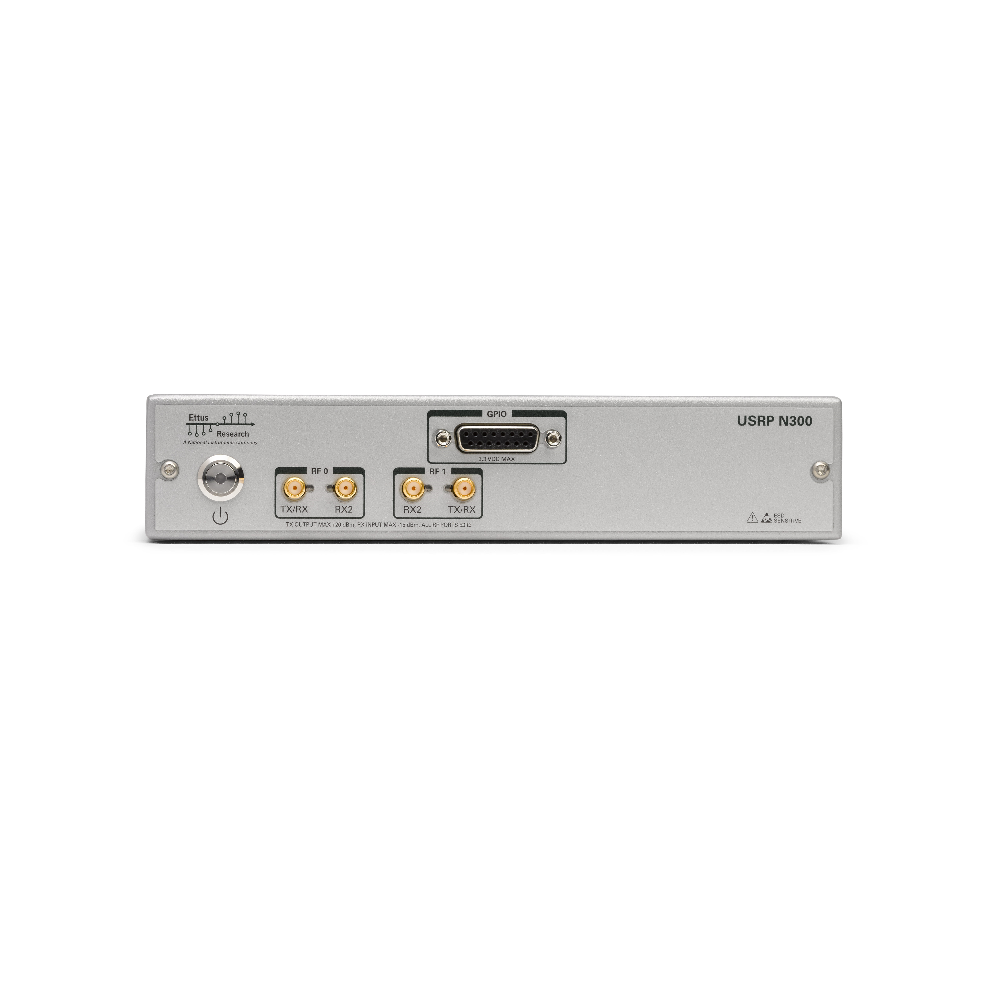
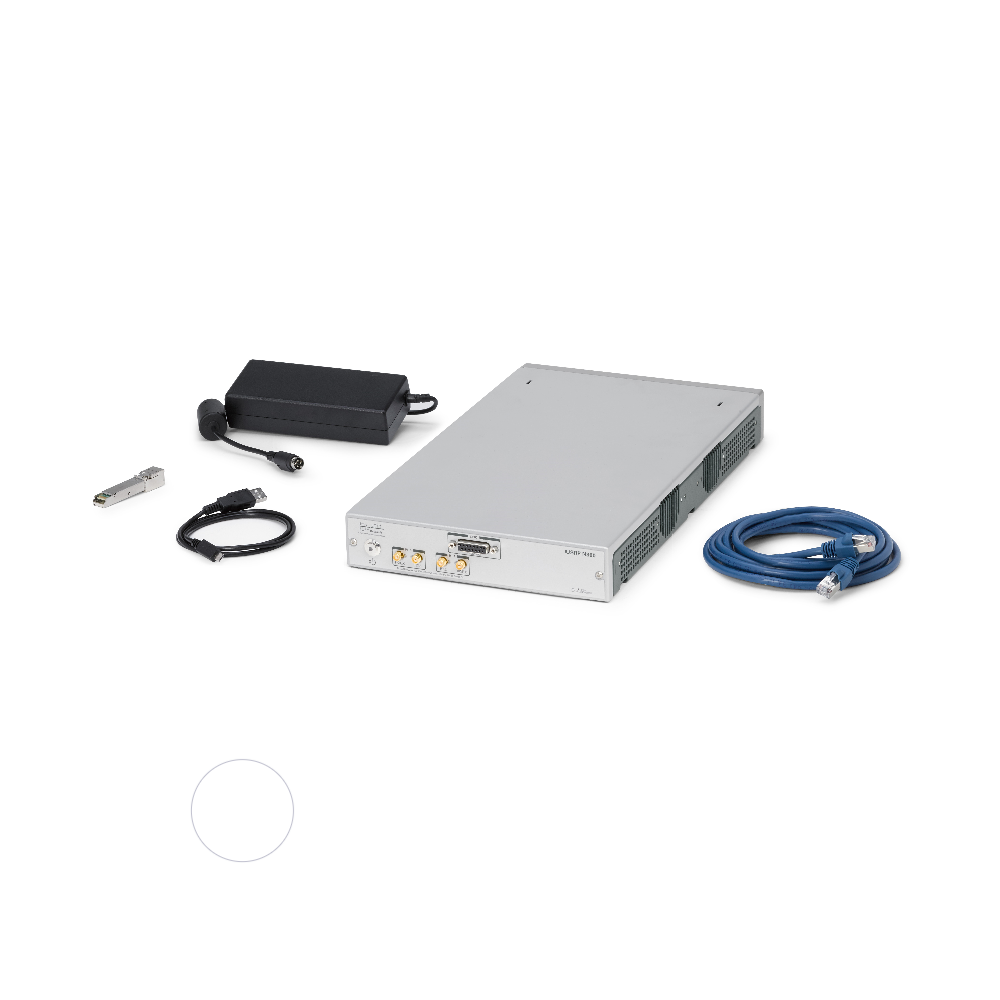
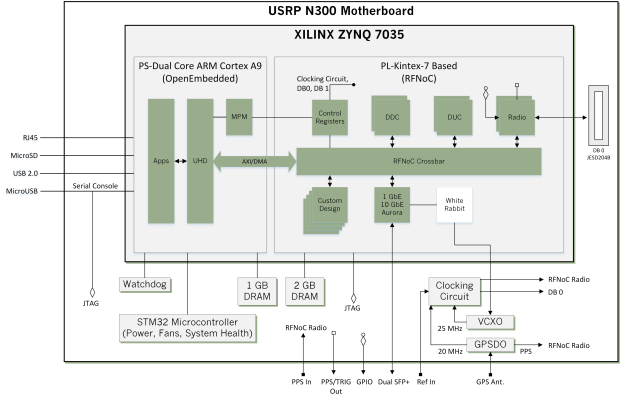
The USRP N300 is a networked software defined radio (SDR) that provides reliability and fault-tolerance for deployment in large-scale and distributed wireless systems. The USRP N300 device simplifies control and management of a network of radios by introducing the unique capability to remotely perform tasks such as updating software, rebooting, factory resetting, self-testing, host PC/ARM debugging and monitoring system health.
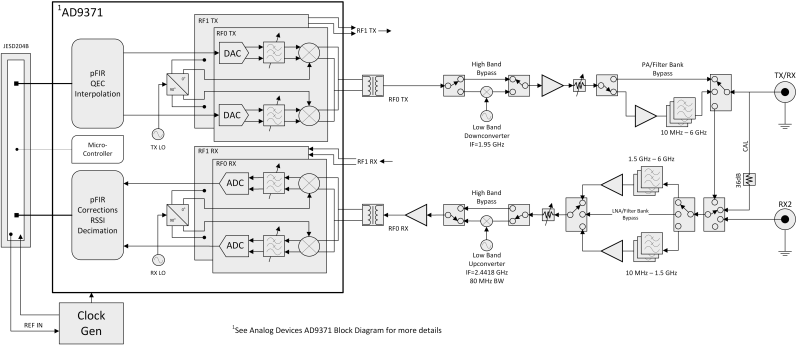
The RF front end uses an AD9371 transceiver, the latest RFIC technology from Analog Devices, to provide 2X2 MIMO capability, up to 100 MHz of instantaneous bandwidth, and an extended frequency range from 10 MHz to 6 GHz.
The open-source USRP Hardware Driver (UHD) API and RF Network-on-Chip (RFNoC) FPGA development framework reduce software development effort and integrate with a variety of industry-standard tools such as GNU Radio. Users can rapidly prototype and reliably deploy designs for a variety of SDR applications such as wireless testbeds, remote radio heads, spectrum monitoring, and more. Please note that the USRP N300 is not designed for fast tuning. For information on products for frequency hopping applications, contact info@ettus.com.
Baseband Processor
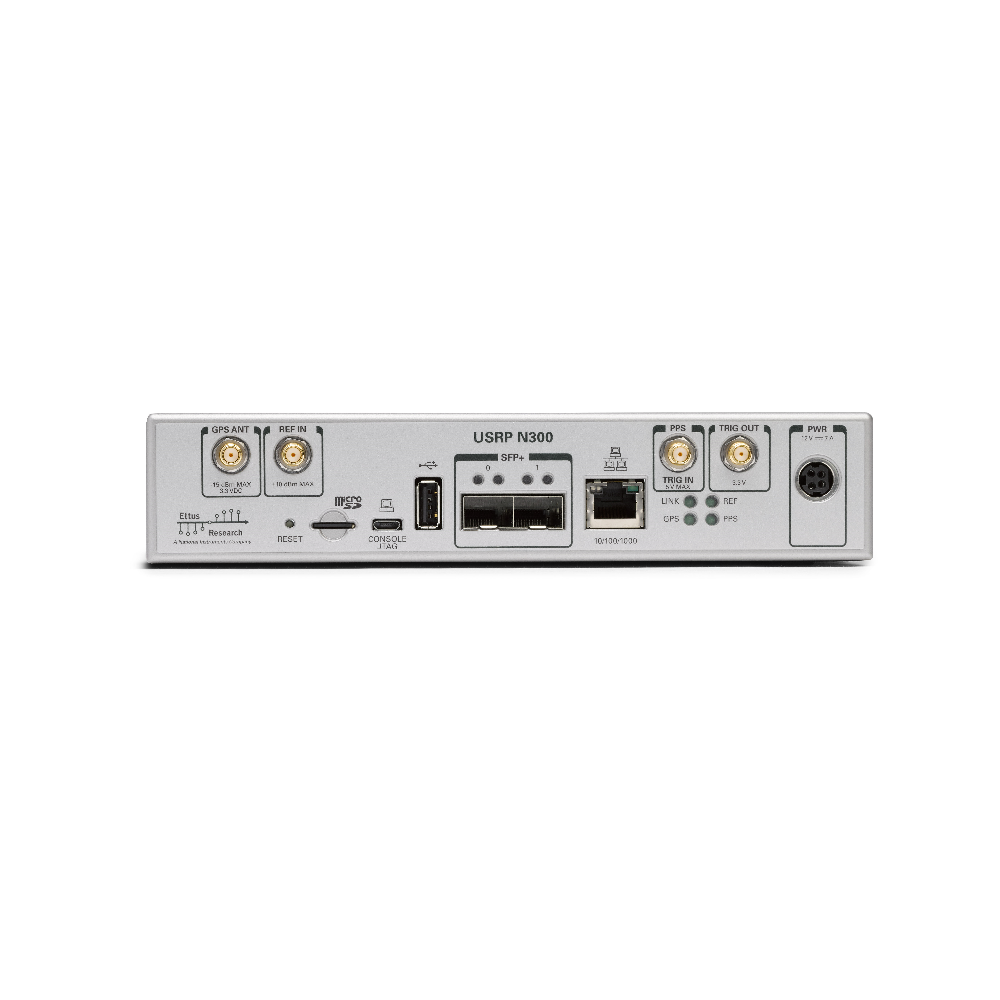
The baseband processor uses the Xilinx Zynq-7035 SoC to deliver a large user-programmable FPGA for real-time and low-latency processing and a dual-core ARM CPU for stand-alone operation. Users can deploy applications directly on to the preinstalled embedded Linux operating system or stream samples to a host computer using high-speed interfaces such as 1 Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gigabit Ethernet, and Aurora over two SFP+ ports.
Synchronization
The USRP N300 has a flexible synchronization architecture with support for traditional SDR synchronization methods such as clock reference, PPS time reference, and GPSDO, which enable implementation of high channel count MIMO systems. In addition, the USRP N300 uniquely features Ethernet-based synchronization using the open-source White Rabbit timing protocol. White Rabbit enables precise baseband synchronization over large distances in GPS-denied environments. For more information, see the “Using Ethernet-Based Synchronization on the USRP N3xx Devices” application note on the Ettus Research Knowledgebase.